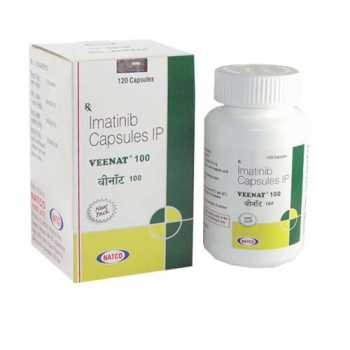
Veenat 100mg (Imatinib)
Courier service EMS
Other transport services
Air India Post International
Payment in the bank on the invoice
WestrUnion
MoneyGram
VEENAT 100MG
Description
Veenat 100mg is used as monotherapy, or it may combine with some other medicine in the conditions of certain types of cancer or bone marrow disorders. PDG-derived tyrosine kinase that is expressed in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
Veenat 100mg indicated for
Veenat 100mg tablet is an anti-neoplastic medicine which is used in the treatment of,
- Advanced myelogenous leukemia (CML),
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and several malignancies
- Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
- Mastocytosis
How Veenat 100mg tablets work
Veenat contains an active component known as Imatinib mesylate, it is an inhibitor of certain tyrosine kinase enzymes.
Veenat prohibits BCR-ABL tyrosine
Veenat obstruct the multiplication and promote the apoptosis in BCR-ABL positive cells in addition to fresh leukemia cells from Philadelphia chromosome positive CML
Veenat also inhibits tumor growth of BCR-ABL transacted murine myeloid cells along with other BCR-ABL positive leukemia CML in blast crisis
Veenat inhibits receptor tyrosine kinase for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), stem cell factor (SCF) and PDGF and SCF mediated cellular events get prohibited.
- Veenat a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine analog, it acts as a prohibition of the tyrosine kinase enzyme.
- In malignancy conditions, Philadelphia chromosome leads to the fusing of protein with BCR (breakpoint cluster region). Veenat used to reduced Bcr-Abl activity.
Absorption:
it is absorbed within 2-4 hours and bioavailability of Veenat 100mg tablets is about 98%.
Distribution:
Veenat 100mg tablet has Human plasma protein bound almost range of 95%.
Metabolism:
Veenat 100mg tablet Active metabolite is N-demethylated piperazine derivative. The enzyme which is responsible for metabolism of Veenat 100mg tablet is CYP3A4.
Excretion:
The elimination of Veenat400mg through feces
The total drug excreted through feces 81% and drug through urine 13% with 7 days
The half lifetime of Veenat and active metabolite N-dimethyl derivative are around 18 and 40 hours respectively
Dosage and administration
The usual dose of tablet Veenat is 400mg or 600mg as a single dose. Whereas 800mg given by dividing the dose into two as 400mg twice daily.
Veenat tablets should be taken with food
The usual dose for following conditions;
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Chronic phase: In newly diagnosed patients, the dose of Veenat 100mg tablet is 400mg should be orally taken as a single dose.
If the failure of chronic phase of the treatment with interferon alpha therapy; dose is raised to 600mg per day.
Quick phase: 600mg PO q Day; dose variation to 400mg PO as twice in a day if there is no serious adverse drug reaction or non-leukemia associated neutropenia or thrombocytopenia.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors
The prescribed dose of the tablet Veenat 100mg is 400mg should be taken orally as a twice daily
Hyperesinophillic syndrome
In this condition, recommended dose is 400mg PO q Day
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
In adults, the prescribed dose is 600mg should be taken orally as a single dose.
Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative diseases
The usual dose is 400mg PO q Day
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Recommended dose is 400mg PO q12hr
In pediatric:
Chronic myeloid leukemia
<1 year: the safety and efficacy of the drug has not been established
≥1 year: 340mg/m2/day PO; should not be exceed 600mg/day
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Patients<1 year: the safety and efficacy of the drug has not been established
Patients≥1 year: 340mg/m2/day PO; should not be exceed 600mg/day
Veenat 100mg tablet causes some side effects
Side effects are common in patients administrating Veenat 100mg-30%
- Nausea and vomiting
- Edema (swelling of the face, feet, hands)
- Muscle cramps and bone pain
- Diarrhea
- Hemorrhage
- Skin rash
- Fever
- Decreased blood counts
Less common side effects occur in patients administrating 10-29%
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Indigestion (see heartburn)
- Abdominal pain
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Poor appetite
- Constipation
- Night sweats (see skin reactions)
- Nosebleeds (see bleeding problems)
- Weakness
- Affect ability to conceive or father a child
Drug-drug interaction
Warfarin is metabolized by CYP2C9 & CYP2A4, so patients who are taking anticoagulation therapy with Veenat, should take low molecular weight or standard heparin in reverse of warfarin.
Drug which inhibits the CYP3A4 activity may have a chance to reduce metabolism and elevates the plasma concentration of Veenat frequently.
Concomitant use of St. John’s wort with Veenat causes decreasing AUC of Veenat to 30%. To avoid this problem, the dosage of Veenat increases up to 1200mg /day (600mg as two times a day).
While the interaction of Veenat with strong inducers of CYP3A4, the dose of Veenat 100mg increased to 50%. If used with CYP3A4 strong inducers the AUC of Veenat 100mg decreases to 73%.
Combination of Veenat 100mg with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors; increase the risk of Veenat. Avoid these co administrations like Veenat 100mg with ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, ritonavir, voriconazole etc.
Interaction of Veenat 100mg with CYP3A4 substrates like alfentanil, cyclosporine, ergotamine, fentanyl, sirolimus or Tacrolimus causes low therapeutic effects. Veenat elevates the plasma concentration of CYP3A4 metabolized drugs like lipid-lowering, calcium channel blockers etc.
Contraindication
Hypersensitive reaction to Veenat 100mg and other excipients presents in Veenat 100mg tablets.
Precaution
Avoid combination of strong CYP3A4 inducers
If anticoagulation is necessary, use LMW or standard heparin instead of warfarin
Gastrointestinal disorders: To avoid this problem, Veenat should be taken with food and large glass of water.
Hyperesinophillic cardiac toxicity
Dermatological toxicities
Hypothyroidism: Levothyroxine replacement therapy recommended; TSH level of the patients should be monitored periodically.
Fluid retention and edema: The major damage of Veenat is a fluid collection which may cause edema majorly superficial edema has been reported. To overcome these problem patients may frequently monitor for manifestation of fluid retention.
Hematological toxicity: Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia are the major blood-related problems. To avoid these conditions, monitor the patients periodically with counting blood cell counts weekly for one month, two weeks for two months.
Serious congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction: Patients who have cardiac problems should be monitored frequently.
Hepatotoxicity: Liver function test should be taken periodically to overcome these problems.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy category: D
Veenat 100mg will cause fetal harm when given to pregnant women
No clinical studies regarding the use of the drug in pregnant women
Lactations
Veenat 100mg should not be recommended to pregnant and breastfeeding mothers, it can able to cause fetal malformations and cause fetal harm
The metabolites excreted in human milk.
Storage condition
Veenat 100mg tablet container should be stored in a cool and dry place
It should be kept away from moisture, heat, and light
Missed Dose
If patient missed to take Veenat 100mg tablet, the patient should have administered within a time. Otherwise, the tablet should be discontinued and follow the next drug schedule.
- Trade name Veenat 100mg
- Substance Imatinib
- Manufacturer Natco Pharma Limited
- Packaging 28 tablets
- Country of origin India
-
Convenient deliveryWe deliver to all countries of the World *. We cooperate only with trusted cargo carriers.
-
CONTROL AND INSPECTIONItem is checked before shipping! All the medicines are delivered directly from the manufacturer and sent from India to the client's address.
-
CHOOSE USWe provide the best price, including insurance against loss through the fault of the carrier. Our company cooperates directly with the largest manufacturers of medicines in India.
-
Promotions and DiscountsWe offer a flexible system of discounts for our customers and fixed discounts for current offers. Regular customers receive a discount of up to 10% of the amount of orders, as well as a remuneration system for referring customers via a referral link.
Запазете любимите си елементи към отметки
Това няма да загуби желаната опция!